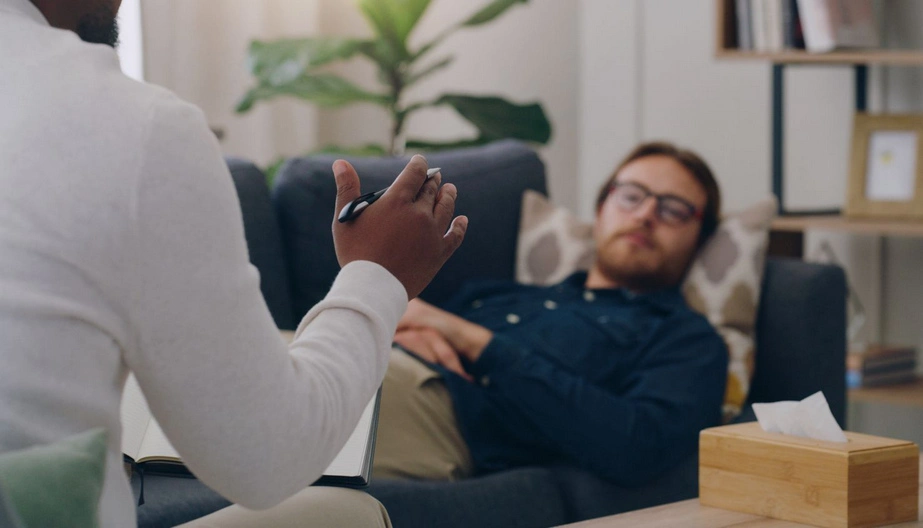
Targeting symptoms, avoiding relapses, and boosting adaptive functioning are all objectives in the treatment for schizophrenia so that the patient can reintegrate into society. To encourage treatment adherence, a psychiatrist will determine the patient’s goals and aspirations and connect them to the treatment outcomes.
Therapy also works to increase the patient’s quality of life by educating the patient and family on coping mechanisms. Antipsychotic medications can help to lessen and control many psychotic symptoms, such as delusions and visual and auditory hallucinations. A combination of therapies and prescription drugs regulate psychosis, reduce anxiety and extreme agitation, and it helps with coherent thoughts and speech. Early schizophrenia interventions aim to promote the best possible recovery and to minimize any negative effects that psychosis may have on a person’s life.